OUR MATERIALS || HARDWOOD || MAPLE WOOD
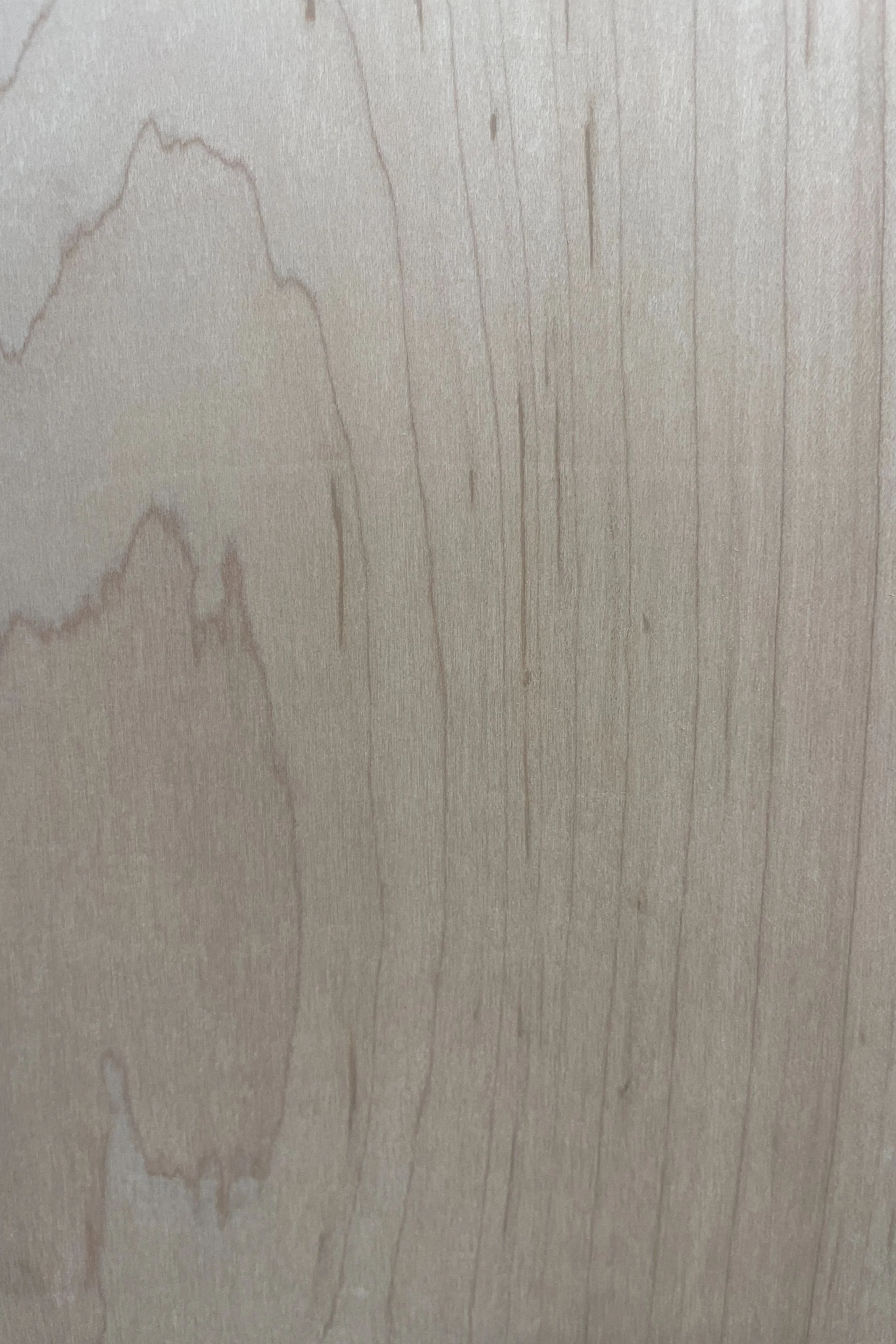
MAPLE WOOD
Alternative Names & Variations: Hard Maple, Soft Maple, Curly Maple, Sugar Maple
Color: Darker Reddish-Brown Heartwood, Nearly White Sapwood
Hardness: Hard
Sustainability Status: Very Sustainable / Stable Species Population
Characteristics: The sapwood of maple wood is predominantly used in various applications due to its lighter color, ranging from nearly white to an off-white cream. In contrast, the heartwood tends to be a darker reddish-brown.
One of the notable features of maple wood is its potential for distinctive figure patterns. Birdseye, curly, and quilted grain patterns enhance the wood's aesthetic appeal and are sought after for specialty woodworking projects.
These characteristics collectively contribute to the overall appeal and versatility of hard maple, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, from flooring and veneer to musical instruments and turned objects.
STRENGTHS
-
Very easy to work with hand and machine tools. Alder wood is soft, sands easily, and finishes well.
-
Alder wood is abundant in the US, making it accessible for small and large-scale projects.
-
Once fully dried, Alder wood is sturdy, exhibiting minimal twisting or alterations in finished products.
-
Alder is more affordable than other hardwoods, making it a great option for budget-minded shoppers.
WEAKNESSES
-
Alder wood is not always the best option in terms of rot resistance. Alder wood is best for indoor furniture; it turns to pulp in moist, warm conditions.
-
Some may exhibit allergies to Alder tree pollen. In extreme cases, sensitivities to wood dust or wood oils may occur.
-
Despite being a hardwood, Alder wood is relatively soft. To protect the finish from knicks and dents, caution is needed against sharp objects.
MAPLE WOOD ALTERNATIVES